Self-Supporting Design for Easy Aerial Installations
The Figure 8 fiber optic cable is a modern solution for fast and reliable data transmission over long distances. Its unique “Figure 8” design features a core fiber optic strand surrounded by a protective reinforcement layer. This design not only provides mechanical strength but also protects the cable from environmental factors. It is particularly ideal for aerial fiber optic installations, allowing the cable to be suspended between poles or towers without the need for additional supporting infrastructure like steel wires. As a result, Figure 8 cables are a cost-effective and convenient choice for large outdoor networks.
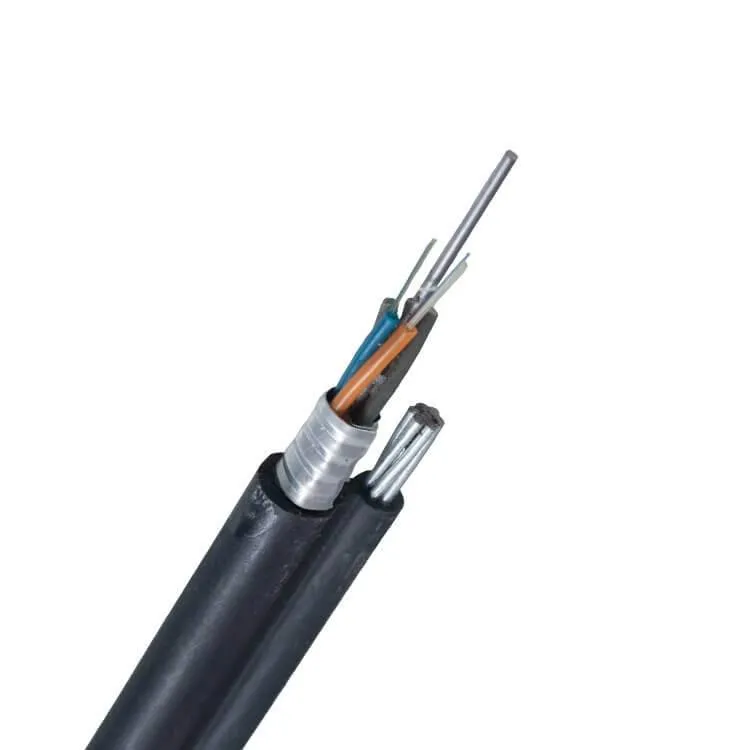

The core of a Figure 8 fiber optic cable is made of high-performance fiber strands that transmit data using light, ensuring fast speeds and minimal signal loss. The central fiber bundle can contain multiple optical fibers, each capable of handling large volumes of data. This makes Figure 8 cables a top choice for broadband internet, telecommunications, and cable TV services.
The outer reinforcement layer, often made from a metal wire or strength member, plays a critical role. It allows the cable to support its own weight over long spans and protects the fibers from damage caused by harsh weather, moisture, or physical stress. This makes Figure 8 cables perfect for use in tough outdoor conditions, such as rural areas or places with extreme weather.
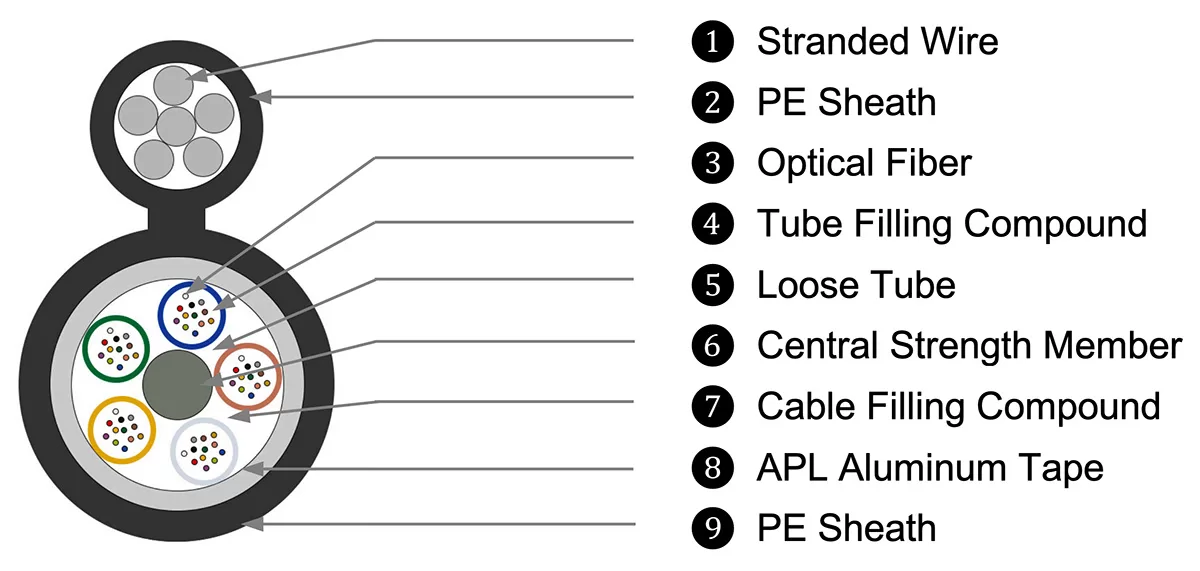
Another key advantage is the cost-efficiency of installation and maintenance. Since Figure 8 cables don’t require external support wires, they are easier and cheaper to install compared to traditional methods. The durability of the cable also means it needs minimal maintenance, reducing long-term operational costs.
In conclusion, the Figure 8 fiber optic cable combines the benefits of high-speed data transfer, environmental durability, and cost-effective installation, making it an essential component for modern telecommunications networks.
