What is Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber optic cable is a revolutionary technology used for transmitting data through light signals, rather than traditional electrical signals. Unlike copper cables, which use electrical current to transfer data, fiber optics rely on light pulses that travel through thin strands of glass or plastic fibers. This unique method allows for high-speed data transmission, making fiber optic cables the backbone of modern telecommunications, internet infrastructure, and many other industries.
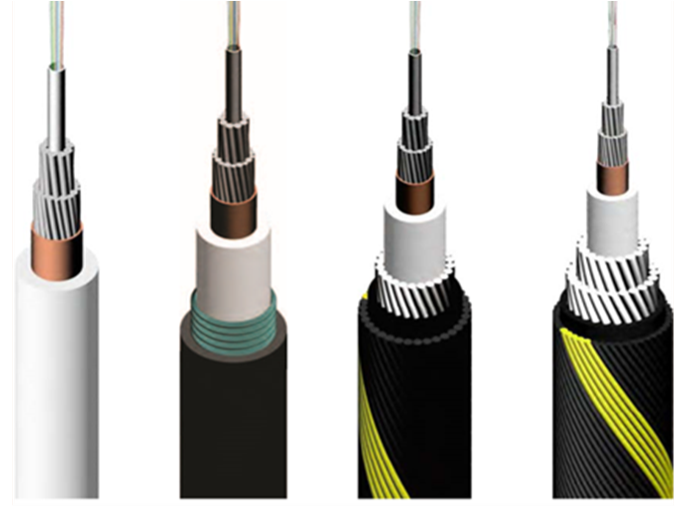

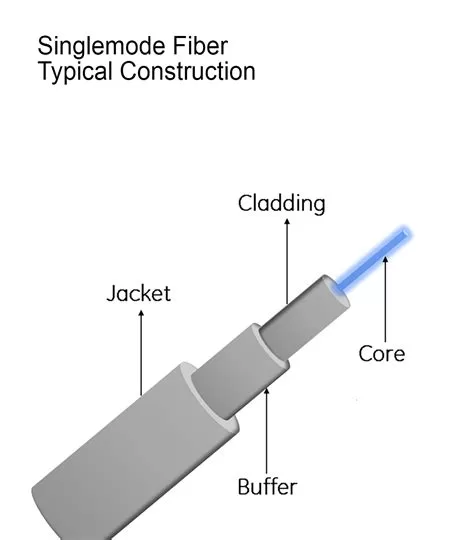
The structure of a fiber optic cable is designed to facilitate the efficient transmission of light signals. The core of the fiber is made of high-purity glass or plastic, through which light travels. Surrounding the core is a layer called the cladding, which reflects light back into the core to keep the signal from escaping. This allows the light signals to travel long distances with little to no signal degradation.
Features of Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables have several key features that make them superior to traditional copper cables. Some of the most important features include:
- High-Speed Data Transmission: Fiber optic cables allow for the transmission of data at incredible speeds. Unlike copper cables that suffer from signal loss over long distances, fiber optics maintain signal integrity and high speeds even over vast distances.
- High Bandwidth Capacity: Fiber optic cables can carry large amounts of data simultaneously, making them ideal for bandwidth-heavy applications such as streaming, video conferencing, and cloud computing.
- Immunity to Interference: One of the most significant advantages of fiber optics is that they are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI), a problem that affects copper cables. This ensures a more stable and reliable connection.
- Security: The light signals used in fiber optics are much harder to intercept or tap into compared to electrical signals in copper cables. This makes fiber optic cables a more secure option for transmitting sensitive data.
- Durability and Flexibility: Fiber optic cables are lightweight, strong, and flexible, which makes them easier to install in various environments. They are also less prone to damage from environmental factors like weather and corrosion.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables
There are primarily two types of fiber optic cables: Single-mode fiber (SMF) and Multi-mode fiber (MMF). These types differ in their construction and application, making each suitable for specific needs.
- Single-Mode Fiber (SMF): Single-mode fiber is designed for long-distance communication. It has a small core size (usually around 8 to 10 microns in diameter) and allows only one mode of light to travel through it. This results in a high-quality signal with minimal loss, making SMF ideal for telecommunications and data transmission over large distances, such as between cities or across countries.
- Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF): Multi-mode fiber has a larger core size (typically 50 to 100 microns) and allows multiple modes of light to travel through it. MMF is better suited for short-distance transmission, such as within buildings or local networks. While MMF offers lower bandwidth and higher signal loss compared to SMF, it is more cost-effective for shorter distances.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables offer numerous benefits that make them the preferred choice for modern communication networks. These advantages include:
- Faster Speeds: Fiber optic cables are capable of transmitting data at speeds of up to 100 Gbps (Gigabits per second) and beyond, making them much faster than traditional copper cables, which are limited to lower speeds.
- Longer Transmission Distances: Unlike copper cables, which experience significant signal degradation over long distances, fiber optic cables can transmit data over tens of kilometers without needing a signal booster. This makes them ideal for long-distance connections, such as undersea cables and cross-country networks.
- Higher Reliability: Fiber optics are less susceptible to environmental conditions, such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and electromagnetic interference. This results in a more reliable and stable connection, particularly in areas with harsh weather conditions.
- Low Latency: Fiber optic cables offer low latency, meaning there is minimal delay in data transmission. This is crucial for real-time applications such as online gaming, video conferencing, and financial transactions.
- Future-Proof: As the demand for higher speeds and more bandwidth continues to grow, fiber optics are expected to support future technological advancements. They are considered a future-proof solution for the increasing need for high-speed internet and data transmission.
- Cost-Effective for Large Volumes of Data: While the initial installation of fiber optic cables can be more expensive than copper cables, they are more cost-effective in the long run due to their higher efficiency, low maintenance, and ability to handle large amounts of data.
- Environmental Benefits: Fiber optic cables consume less energy for data transmission compared to copper cables. This reduces their carbon footprint, making them a more environmentally friendly choice for communication networks.
Conclusion
Fiber optic cables are transforming the way we communicate and access information. With their high-speed data transmission, immunity to interference, and security features, fiber optics are becoming the standard for internet, telecommunications, and other industries. Whether used for long-distance communication or local networks, fiber optic cables provide the speed, reliability, and scalability needed for today’s data-driven world. As technology continues to evolve, fiber optics will remain a cornerstone of global connectivity, enabling faster, more efficient, and more secure communication for years to come.
